Prerequisites
- Azure Subscription: Ensure you have an active Azure subscription.
- Set Up Azure Health Data Services: Deploy an instance of Azure API for FHIR or FHIR service in Azure Health Data Services.
- Understand HL7 v2 and FHIR Standards: Familiarize yourself with HL7 v2 message structure and FHIR R4 resources.
- Install Necessary Tools: Install the Azure CLI, FHIR Converter, and related dependencies.
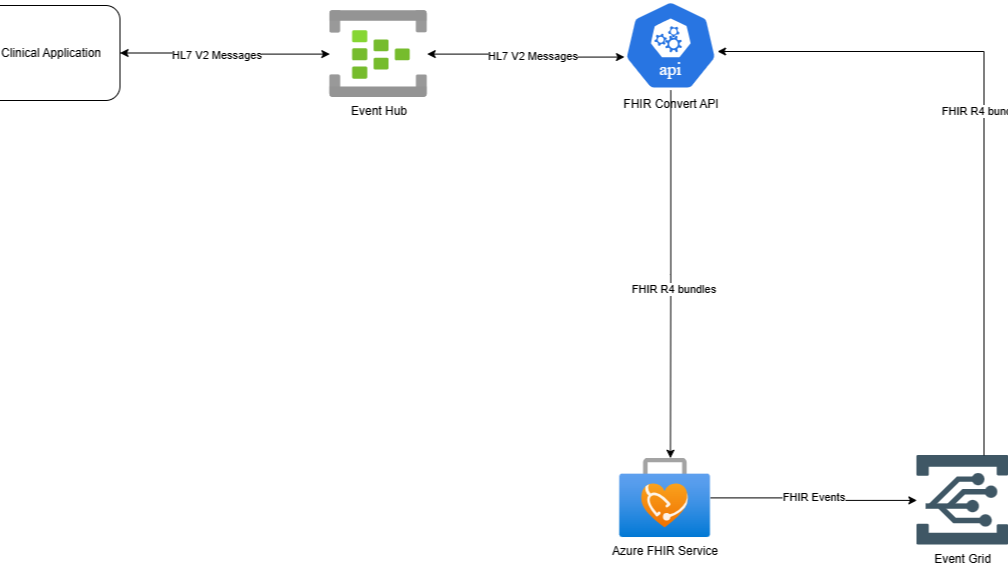
Architecture Overview
Data Flow
- HL7 v2 Messages → FHIR Service: HL7 v2 messages are ingested and converted to FHIR R4 bundles.
- FHIR Server → Legacy System: Updates made in the FHIR server are converted back to HL7 v2 format and sent to the legacy system.
Key Components
- FHIR Service (Azure Health Data Services).
- FHIR Converter: Transforms HL7 v2 messages to FHIR R4 resources and vice versa.
- Event Hubs/Logic Apps: For message ingestion and routing.
- Custom APIs/Adapters: For bidirectional communication between the FHIR server and the legacy system.
Step 1: Ingest HL7 v2 Messages
- Set Up an HL7 v2 Listener: Use Azure Logic Apps or Event Hubs to listen for incoming HL7 v2 messages from the legacy system. Example using Event Hubs: Configure an Event Hub namespace. Create a dedicated Event Hub for HL7 v2 messages.
- Secure Message Transmission: Use TLS for secure communication. Configure authentication mechanisms such as Azure Managed Identity.
- Validate HL7 v2 Messages: Use HL7 validators to ensure message integrity and compliance with HL7 standards.
- Store Messages Temporarily: Use Azure Blob Storage or a queue for temporary storage, enabling reprocessing if needed.
Step 2: Convert HL7 v2 Messages to FHIR R4
- Deploy the FHIR Converter: Use Azure’s FHIR Converter tool to transform HL7 v2 messages into FHIR R4 resources. Clone the FHIR Converter repository and deploy it in an Azure Function or App Service.
- git clone https://github.com/microsoft/FHIR-Converter.git
- Create Custom Mappings: Map HL7 v2 message segments (e.g., PID, OBX) to corresponding FHIR resources (e.g., Patient, Observation). Customize mappings using the FHIR Converter templates.
- Test Conversions: Test sample HL7 v2 messages using the FHIR Converter API. Verify the generated FHIR bundles for accuracy.
- Integrate with Logic Apps: Use Azure Logic Apps to invoke the FHIR Converter for each incoming HL7 v2 message. Pass the converted FHIR bundle to the Azure FHIR service.
Step 3: Store and Process FHIR Data
- Configure the FHIR Service: Deploy the FHIR server using Azure Health Data Services. Set up SMART on FHIR applications if required.
- Store FHIR Resources: Use the FHIR server’s API to store and manage resources such as Patient, Encounter, Observation, etc.
- Implement Business Rules: Develop custom logic for resource validation, deduplication, and notifications using Azure Functions or other middleware.
Step 4: Update Clinical System from FHIR Service
- Monitor Changes in FHIR Service: Use Azure Event Grid to subscribe to resource change events in the FHIR service. Capture create, update, or delete events for relevant resources.
- Convert FHIR to HL7 v2: Configure the FHIR Converter to map FHIR resources back to HL7 v2 messages. Customize templates for HL7 v2 output.
- Send HL7 v2 Messages: Use Logic Apps or Event Hubs to route the converted HL7 v2 messages back to the legacy system. Ensure the legacy system can receive and process these messages correctly.
Step 5: Implement Security and Compliance
- Secure Data Transmission: Use HTTPS and OAuth 2.0 for FHIR API communication. Enable role-based access control (RBAC) for the FHIR service.
- Ensure HIPAA/GDPR Compliance: Implement auditing for all FHIR transactions. Use Azure Monitor and Log Analytics for tracking data flows and identifying anomalies.
- Encrypt Data: Use Azure Key Vault to manage encryption keys. Encrypt data at rest and in transit.
Step 6: Testing and Validation
- Unit Tests: Validate individual components such as the FHIR Converter mappings and Logic Apps workflows.
- Integration Tests: Simulate end-to-end data flow from the legacy system to the FHIR service and back.
- Performance Tests: Test the system under load using Azure Load Testing tools.
Step 7: Monitoring and Maintenance
- Set Up Monitoring: Use Azure Monitor and Application Insights to track performance and identify issues.
- Automate Alerts: Configure alerts for failures in HL7 ingestion, FHIR conversions, or updates to the legacy system.
- Routine Updates: Periodically update mappings, templates, and FHIR Converter components to comply with evolving standards.
Step 8: Deployment
Rollback Plan: Implement a rollback strategy for safe deployment.
Dev/Test/Prod Environments: Maintain separate environments for development, testing, and production. Use Azure DevOps or GitHub Actions for CI/CD pipelines.
Leave a Reply